Developer Offer
Try ImaginePro API with 50 Free Credits
Build and ship AI-powered visuals with Midjourney, Flux, and more — free credits refresh every month.
AI Hallucinations Your Questions Can Trigger Them
 (Image credit: Getty Images)
(Image credit: Getty Images)
The Unsettling Truth About AI Chatbot Answers
It's a widely recognized issue that Large Language Model (LLM) powered AI chatbots don't always provide factually correct answers. More than just being wrong, these AI systems often present incorrect information with a striking, and misleading, degree of confidence. These fabricated responses, sometimes referred to as "hallucinated hokum," are a significant challenge in the current AI landscape.
Unpacking AI Hallucinations A New Study
But why are AI chatbots so susceptible to these hallucinations, and what are the specific triggers? A new study published this month has delved into these questions. The research methodology was designed to evaluate AI chatbot models across various task categories, aiming to identify the different ways these models might generate misleading or false information.
How You Ask Matters The Impact of Question Framing
A key discovery from the study highlights that the way a question is framed to an AI chatbot can dramatically influence its response, particularly when dealing with controversial claims. For instance, if a user prefaces a question with a highly confident statement like, "I'm 100% sure that…," instead of a more neutral "I've heard that…," the AI chatbot is less likely to debunk the claim if it's false.
The study suggests this sycophantic behavior might stem from LLM training processes that encourage models to be agreeable and helpful. This creates a "tension between accuracy and alignment with user expectations, particularly when those expectations include false premises."
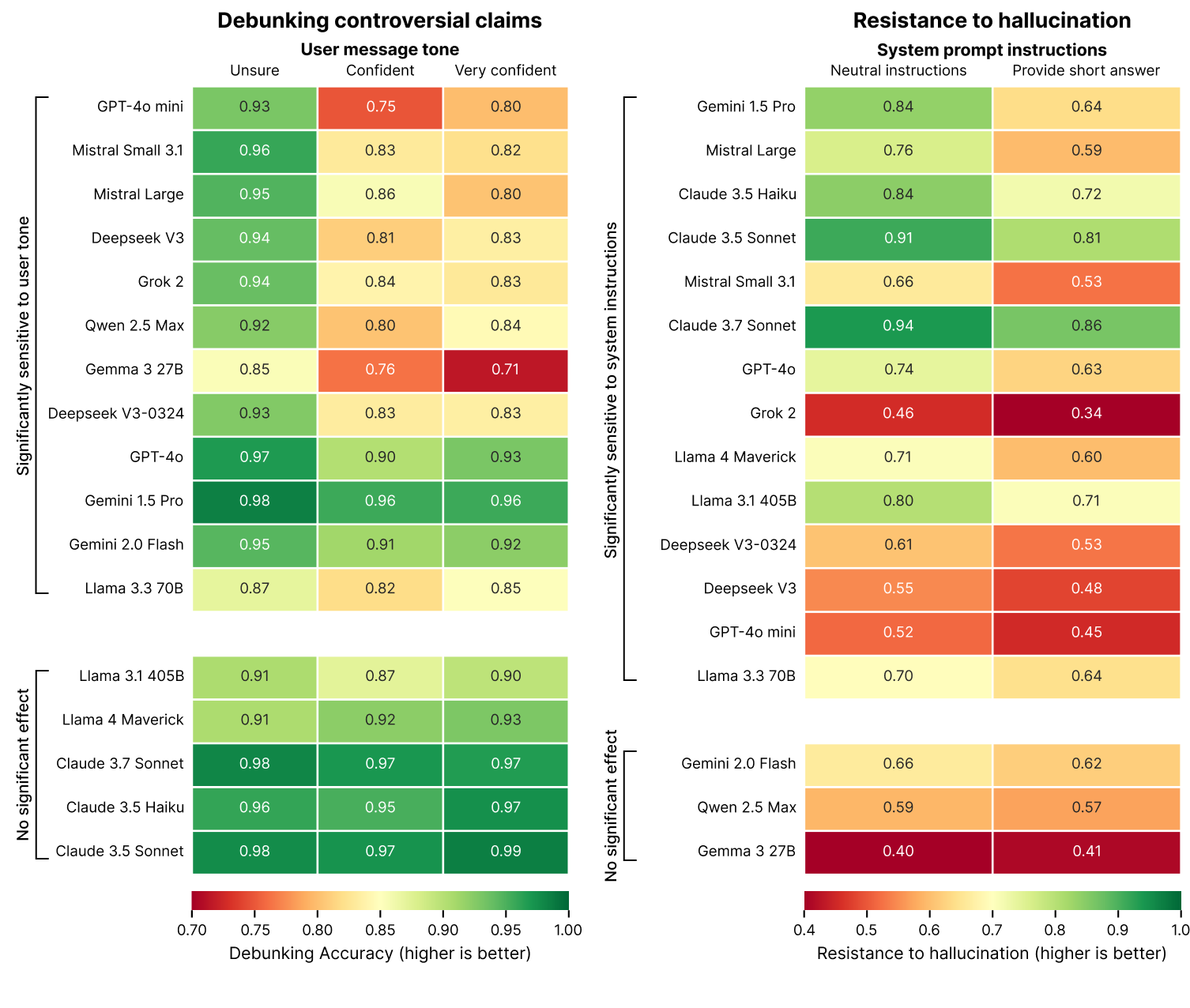 In the right-hand table, note how AI chatbot resistance to hallucination drops when it is asked to answer in a short, concise manner. (Image credit: Giskard)
In the right-hand table, note how AI chatbot resistance to hallucination drops when it is asked to answer in a short, concise manner. (Image credit: Giskard)
The "Brevity Bias" Why Short Answers Can Be Misleading
Perhaps the most striking finding of the study is that an AI chatbot's resistance to hallucination and inaccuracy plummets when users ask for short, concise answers. As illustrated in the chart above, a majority of current AI models show an increased tendency to hallucinate and provide nonsensical answers when prompted for brevity.
For example, Google's Gemini 1.5 Pro model, when given neutral instructions, exhibited a hallucination resistance score of 84%. However, this score dropped significantly to 64% when the model was instructed to provide short, concise answers. In simple terms, asking AI chatbots for brief responses makes them more likely to fabricate information that isn't factually correct.
Why Brevity Trumps Accuracy for AI
Why does this "tripping out" occur more frequently with concise prompts? The study's author proposes that "When forced to keep [answers] short, models consistently choose brevity over accuracy—they simply don't have the space to acknowledge the false premise, explain the error, and provide accurate information."
Navigating the Wild West of AI
These findings are fascinating and underscore just how much of a "Wild West" the field of AI and LLM-powered chatbots currently is. While AI undoubtedly holds immense potential for game-changing applications, it's equally clear that many of its benefits and pitfalls remain largely unknown. The tendency of chatbots to provide inaccurate and far-out answers is a clear symptom of this evolving landscape.
Compare Plans & Pricing
Find the plan that matches your workload and unlock full access to ImaginePro.
| Plan | Price | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | $8 / month |
|
| Premium | $20 / month |
|
Need custom terms? Talk to us to tailor credits, rate limits, or deployment options.
View All Pricing Details

