Developer Offer
Try ImaginePro API with 50 Free Credits
Build and ship AI-powered visuals with Midjourney, Flux, and more — free credits refresh every month.
AI Excels at Medical Image Exams with GPT4o
The Rise of AI in Medical Education
Generative artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT are rapidly changing numerous fields, and medical education is no exception. Advanced models such as GPT-4 and the newer GPT-4 Omni (GPT-4o) have shown a remarkable ability to understand complex text and reason through problems. Their potential to help with clinical decision-making, exam preparation, and streamlining the learning process is significant.
While previous studies have shown that AI can perform well on text-based medical exams, a crucial gap remained: its ability to handle questions that include clinical images. In fields like dermatology, radiology, and pathology, visual diagnosis is fundamental. This study addresses that gap by evaluating how well GPT-4 and GPT-4o can interpret and answer image-based questions from the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), a benchmark for medical knowledge.
Putting AI to the Test The USMLE Challenge
To create a rigorous test, researchers gathered all 38 publicly available image-based questions from the USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 Clinical Knowledge sample sets. These questions are designed by the National Board of Medical Examiners to assess a combination of foundational medical knowledge and practical clinical reasoning. They cover a wide range of specialties and represent the types of challenges that doctors face daily.
Each AI model was presented with the questions one by one in a fresh session to avoid any memory effects. Using specific prompts, the models were asked to provide a single answer choice without an explanation, mimicking a standard exam environment. This method allowed for a clear calculation of their accuracy based on the number of correct responses. The study also explored how these models could be used in case-based teaching scenarios, further probing their utility for educators.
The Verdict How Did GPT-4 and GPT-4o Perform
The study analyzed 38 questions spanning 18 medical disciplines, with dermatology, cardiology, and gastroenterology being the most represented. The results showed a significant leap in performance with the newer model.
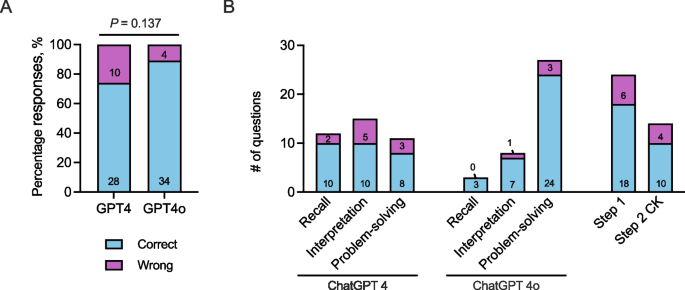
GPT-4 achieved a respectable accuracy rate of 73.4%. However, GPT-4o performed even better, correctly answering an impressive 89.5% of the image-based questions. While this improvement was notable, the difference was not statistically significant, likely due to the limited number of questions. Interestingly, the four questions that GPT-4o answered incorrectly were also missed by GPT-4, suggesting that certain complex visual reasoning tasks remain a challenge for current AI.
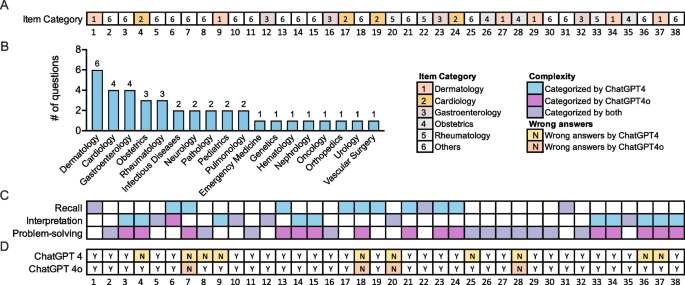
An interesting side-note was that the two models often disagreed on the complexity of the questions, with only about half being classified identically.
Beyond the Exam AI as a Teaching Assistant
The potential of these AI models extends far beyond simply taking tests. The study demonstrated that Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) like GPT-4o can be valuable tools for educators. For example, they can help generate new multiple-choice questions from existing course materials that include images, streamlining the development of assessments.
Furthermore, GPT-4o showed a strong capacity for logical reasoning when asked to analyze incorrect answers. This suggests it could be used to create detailed explanations that help students understand their mistakes and reinforce key clinical concepts. In exploratory tests, the model was also able to assist in designing structured lesson plans centered on specific clinical cases, showcasing its potential to make curriculum development more efficient.
A Cautious Welcome The Future of AI in Medicine
This study provides compelling evidence that AI is becoming increasingly capable of handling complex, multimodal medical tasks. The high accuracy of GPT-4o on image-based USMLE questions signals a new frontier for AI-assisted learning.
However, the researchers stress the importance of caution and continued human oversight. Errors still occur, especially in nuanced clinical scenarios, which means that any AI-generated educational content must be validated by experts to ensure it is accurate, safe, and pedagogically sound. The study also acknowledges limitations, such as the small sample size and the use of a web interface instead of a more controlled API. Despite these limitations, the findings strongly support the growing role of AI as a powerful assistant in medical education. The future lies not in replacing human instructors, but in integrating these advanced tools to create a more efficient and personalized learning experience for the next generation of healthcare professionals.
Compare Plans & Pricing
Find the plan that matches your workload and unlock full access to ImaginePro.
| Plan | Price | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | $8 / month |
|
| Premium | $20 / month |
|
Need custom terms? Talk to us to tailor credits, rate limits, or deployment options.
View All Pricing Details

