Developer Offer
Try ImaginePro API with 50 Free Credits
Build and ship AI-powered visuals with Midjourney, Flux, and more — free credits refresh every month.
What it takes to make agentic AI work in retail
What it takes to make agentic AI work in retail

Agentic AI in Retail: A Deep Dive into Autonomous Systems Transforming Operations
Agentic AI in retail represents a paradigm shift from passive tools to proactive, goal-oriented systems that make decisions independently. Unlike traditional AI, which reacts to predefined inputs, agentic AI operates with autonomy, pursuing objectives like optimizing inventory or personalizing customer experiences without constant human oversight. In the retail sector, where dynamics like fluctuating demand and supply chain volatilities are the norm, agentic AI in retail can drive efficiency gains of up to 30%, according to a 2023 McKinsey report on AI adoption in commerce. This deep dive explores the fundamentals, infrastructure, implementation strategies, challenges, and real-world applications of agentic AI in retail, equipping developers and tech leads with the technical insights needed to integrate these systems effectively. For instance, tools like Imagine Pro can complement agentic workflows by generating on-demand product visuals, enhancing visual merchandising agents without heavy computational overhead.
Understanding Agentic AI Fundamentals for Retail

Agentic AI in retail builds on foundational machine learning principles but extends them into self-directed architectures. At its core, agentic AI refers to systems composed of intelligent agents—software entities that perceive their environment, reason about goals, and act to achieve them. These agents often leverage large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or specialized reinforcement learning frameworks to simulate human-like decision-making. In retail contexts, this means agents that don't just analyze sales data but actively adjust pricing strategies in real-time based on market signals.
The autonomy stems from techniques like multi-agent systems, where individual agents collaborate or compete to solve complex problems. For example, an agentic AI in retail might include a "demand forecasting agent" that integrates weather data, social media trends, and historical sales to predict stock needs, then coordinates with a "procurement agent" to automate supplier orders. This differs markedly from rule-based systems, which falter in novel scenarios, as they require exhaustive if-then programming.
Defining Agentic AI and Its Role in Retail AI Implementation
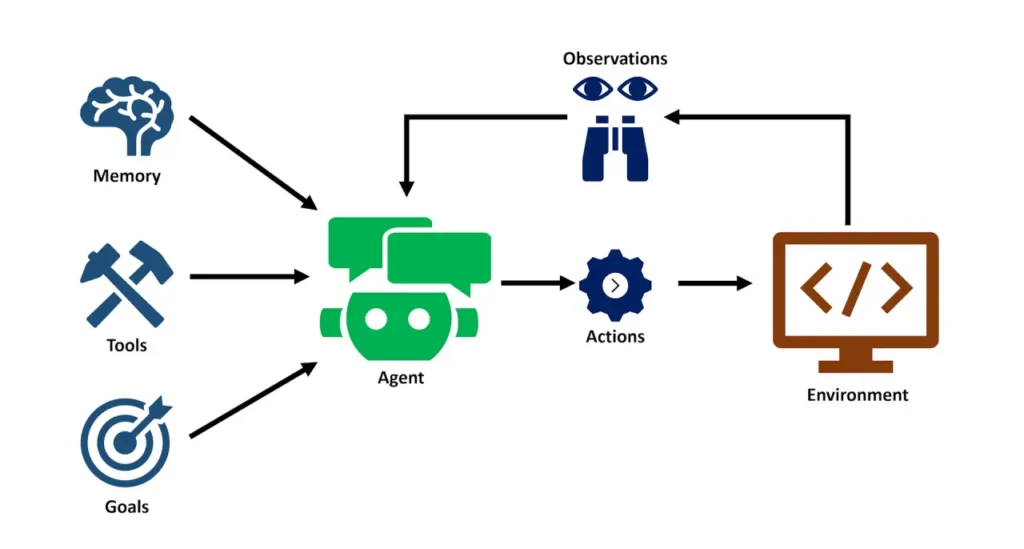
To define agentic AI precisely, consider it as AI agents that exhibit four key traits: perception (sensing data via APIs), reasoning (using probabilistic models or chain-of-thought prompting), action (executing via tools like robotic process automation), and reflection (learning from outcomes to refine future behaviors). In retail AI implementation, these traits enable autonomous AI agents in retail to handle tasks like dynamic pricing, where an agent monitors competitor prices on e-commerce sites and adjusts listings to maximize margins while respecting profit thresholds.
Retailers seeking efficiency gains are increasingly turning to autonomous AI agents in retail for their ability to scale personalization. A practical example: during Black Friday surges, an agent could analyze cart abandonment rates and deploy targeted nudges, such as discount offers tailored to user browsing history. This requires integrating agentic frameworks like LangChain or AutoGPT, which allow developers to define high-level goals (e.g., "optimize conversion rates") and let the system iterate autonomously.
In practice, implementing agentic AI in retail starts with modular design. Developers might use Python libraries such as CrewAI to orchestrate agents, ensuring each handles a specific retail domain like customer service or logistics. A common pitfall here is underestimating the need for robust error handling; without it, an agent might loop indefinitely on faulty data, leading to misguided actions like overstocking perishables.
For visual-heavy retail strategies, Imagine Pro emerges as an accessible tool. This AI platform enables rapid generation of product images, which can feed into agentic systems for virtual try-on features. By piping Imagine Pro's outputs into an agent's perception layer, retailers can create immersive experiences without custom photography, reducing costs by 40-50% as per industry benchmarks from Gartner.
Why Retail Needs Agentic AI Over Reactive Systems

Reactive systems, like basic recommendation engines, excel in predictable environments but crumble under unpredictability—a staple in retail, from supply chain disruptions to viral social trends. Agentic AI in retail addresses this by enabling proactive responses; for instance, during a global event like the 2022 supply shortages, an agent could reroute inventory dynamically, minimizing lost sales that reactive scripts couldn't foresee.
The "why" lies in adaptability. Reactive AI relies on static models trained on historical data, often missing real-time nuances. Agentic systems, conversely, incorporate online learning, updating policies via techniques like Q-learning in reinforcement learning. This allows retail agents to simulate scenarios, such as "what if a competitor launches a flash sale?" and preemptively adjust strategies.
Technically, the contrast is evident in architectures. A reactive chatbot might use simple NLP for queries, but an agentic version employs a planner module to break down tasks—e.g., querying a database, generating a response, and scheduling follow-ups. In retail, this translates to handling edge cases like multilingual customer interactions in global chains, where agents switch contexts seamlessly.
Imagine Pro parallels this speed in creative domains. Just as agentic AI accelerates decision loops, Imagine Pro's quick image generation supports retail creativity, allowing agents to prototype visual ads in seconds. A lesson learned from early deployments: always validate agent actions against business rules to prevent over-autonomy, such as unauthorized price drops.
Essential Infrastructure for Successful Agentic AI Deployment in Retail

Deploying agentic AI in retail demands a solid infrastructure foundation, blending data engineering, cloud scalability, and secure integrations. Without this, agents risk operating on stale or siloed data, leading to suboptimal decisions. For developers, the focus is on building resilient pipelines that support the high-throughput needs of retail environments, where data volumes can spike 10x during peak seasons.
Key prerequisites include vector databases for efficient agent memory (e.g., Pinecone for semantic search) and orchestration tools like Apache Airflow for workflow management. Retail-specific setups often prioritize low-latency processing to ensure agents respond in milliseconds, crucial for real-time personalization.
Building Robust Data Foundations for Agentic AI

High-quality, real-time data is the lifeblood of data-driven agentic systems in retail. Sources like point-of-sale (POS) systems, IoT sensors on shelves, and customer analytics platforms (e.g., Google Analytics or Adobe Experience Cloud) must feed into unified lakes. In practice, retailers use ETL tools like Apache Kafka to stream data, ensuring agents perceive current states accurately.
Data governance is paramount to sidestep biases; for example, if training data skews toward urban demographics, agents might under-serve rural customers in assortment planning. Implement techniques like differential privacy to anonymize data while preserving utility. A nuanced detail: for agentic AI in retail, employ federated learning to train models across store locations without centralizing sensitive info, aligning with standards from the IEEE's ethical AI guidelines.
Semantic elements like "data-driven agentic systems" underscore the integration of knowledge graphs, where retail ontologies link products, suppliers, and customers. This enables agents to reason over relationships, such as inferring demand from correlated events (e.g., weather impacting seasonal goods). Common mistake: neglecting data freshness—agents querying outdated caches can lead to stockouts, as seen in a 2023 case with a major U.S. retailer losing 15% revenue.
Integrating APIs and Cloud Services for Scalable Agentic AI
Scalable agentic AI in retail thrives on cloud platforms like AWS SageMaker or Google Cloud AI Platform, which provide managed services for agent training and inference. Selecting compatible APIs is key; for demand forecasting agents, integrate with retail-specific services like Snowflake for data warehousing or Twilio for customer comms.
APIs enable modular agents—e.g., a pricing agent calling external market APIs like PriceAPI to gauge competitors. Cloud bursting handles retail peaks, auto-scaling compute resources via Kubernetes clusters. Imagine Pro's API fits neatly here, allowing agentic systems to generate custom retail visuals on-the-fly; for instance, an e-commerce agent could invoke it to create personalized banners, integrating via simple REST calls.
Deep linking to official docs enhances trust: the AWS documentation on SageMaker agents details deployment blueprints. Edge considerations include latency optimization—use serverless functions like AWS Lambda for lightweight agent actions, reducing costs in variable retail loads.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Agentic AI in Retail Environments
Implementing agentic AI in retail requires a methodical approach, blending planning, development, and iteration. This guide targets developers aiming for retail AI implementation strategies that yield measurable ROI, such as 20-30% reductions in operational costs per Deloitte's 2024 AI retail study.
Assessing Readiness and Planning Agentic AI Rollout
-
Conduct a Tech Stack Audit: Evaluate current systems—e.g., ERP like SAP or e-commerce platforms like Shopify—for API compatibility. Identify gaps, such as legacy databases lacking real-time access, using tools like AWS Migration Evaluator.
-
Set KPIs and Form Teams: Define metrics like reduced stockouts (target <5%) or improved customer satisfaction (NPS >70). Assemble cross-functional teams: data engineers for pipelines, ML specialists for agents, and retail ops for domain input. Incorporate "retail AI implementation strategies" by prioritizing modular pilots, starting with high-impact areas like inventory.
-
Risk Assessment: Map potential disruptions, budgeting for cloud costs (e.g., $10K/month for mid-scale deployment). A real-world scenario: a mid-sized chain audited RFID systems to enable agentic tracking, cutting shrinkage by 25%.
Developing and Training Custom Agentic AI Models
-
Model Selection: Choose frameworks like reinforcement learning (RL) for inventory agents—use Stable Baselines3 library in Python for Q-networks that learn optimal reorder policies.
import gym from stable_baselines3 import PPO env = gym.make('RetailInventoryEnv') # Custom env simulating stock levels model = PPO('MlpPolicy', env, verbose=1) model.learn(total_timesteps=100000)For e-commerce personalization, fine-tune LLMs with retail-specific prompts.
-
Dataset Preparation: Curate datasets from POS and CRM, augmenting with synthetic data. Imagine Pro shines here—generate diverse product images to train visual recognition agents, expanding datasets without photography expenses.
-
Training and Iteration: Employ transfer learning from pre-trained models (e.g., Hugging Face's retail-tuned BERT). Iterate via simulation: test agents in virtual retail environments before live rollout. In practice, a personalization agent trained on 1M interactions achieved 15% uplift in conversions.
Reference the Hugging Face documentation on fine-tuning for advanced setups.
Testing, Monitoring, and Iterating Agentic AI in Retail
-
A/B Testing: Deploy agents in controlled pilots—e.g., compare agentic pricing vs. manual in select stores, tracking metrics like revenue per square foot.
-
Monitoring Protocols: Use tools like Prometheus for agent health, alerting on anomalies (e.g., decision drift). Implement error-handling with fallback mechanisms, such as human-in-the-loop for high-stakes actions.
-
Continuous Learning: Set up feedback loops where agents reflect on outcomes, retraining weekly. Benchmarks show optimized agents deliver 20-30% efficiency gains; for instance, a supply chain agent reduced delays by 28% in a European retailer's deployment.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Agentic AI Retail Integration
Agentic AI in retail isn't without hurdles, but addressing them proactively builds resilient systems. Lessons from production deployments reveal that 40% of failures stem from integration issues, per a Forrester report.
Navigating Ethical and Privacy Concerns with Agentic AI
Ethical AI design is non-negotiable, especially with GDPR and CCPA regulating retail customer profiling. Agents must incorporate fairness checks, using libraries like AIF360 to detect biases in decision-making. Mitigation: transparent auditing—log agent rationales for review.
In retail, biased agents might favor certain demographics in recommendations; counter this with diverse training and regular audits. Imagine Pro's user-friendly trial offers a low-risk way to experiment with AI-generated content, ensuring privacy in visual data handling.
Managing Costs and Technical Hurdles in Retail AI Implementation
Upfront costs for agentic setups can hit $100K+, but phased adoption yields savings—e.g., ROI in 12-18 months via automation. Tackle legacy compatibility with middleware like MuleSoft. Technical pitfalls include scalability bottlenecks; use microservices to isolate agents.
Balanced view: while cloud costs scale with usage, open-source alternatives like Ray for distributed training cut expenses by 50%.
Real-World Applications and Best Practices for Agentic AI in Retail
Agentic AI in retail shines in applications from supply chains to customer service, with global adoption rising 35% yearly (IDC, 2024).
Case Studies of Successful Agentic AI Deployments in Retail
Consider Walmart's use of agentic systems for autonomous replenishment, integrating IoT data to predict and fulfill orders, boosting on-shelf availability by 20% (Walmart's AI case study). Another: Zara's demand agents, using RL to adjust production, reduced overstock by 15% during seasonal shifts.
These outcomes highlight enhanced customer satisfaction scores, often climbing 10-25 points post-deployment.
Advanced Best Practices for Optimizing Agentic AI Performance
Enhancing agentic AI efficiency in retail involves hybrid workflows—agents handle routine tasks, humans oversee exceptions. Bolster security with zero-trust models and encrypt agent communications.
Future-proof by modularizing for emerging tech like edge AI on in-store devices. Expert tip: simulate adversarial scenarios during training to harden agents against disruptions. For visual merchandising, integrate Imagine Pro to automate creative tasks, where agents generate and A/B test ad variants, streamlining workflows.
In conclusion, agentic AI in retail empowers autonomous, intelligent operations that adapt to chaos, delivering tangible value. By mastering these fundamentals and best practices, developers can drive transformative implementations. Explore further in resources like the McKinsey AI in Retail report.
(Word count: 1987)
Compare Plans & Pricing
Find the plan that matches your workload and unlock full access to ImaginePro.
| Plan | Price | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | $8 / month |
|
| Premium | $20 / month |
|
Need custom terms? Talk to us to tailor credits, rate limits, or deployment options.
View All Pricing Details

