Developer Offer
Try ImaginePro API with 50 Free Credits
Build and ship AI-powered visuals with Midjourney, Flux, and more — free credits refresh every month.
Chinese AI Models Match ChatGPT in Medical Performance
The Rise of AI in Clinical Practice
Artificial intelligence (AI), a concept born in 1956, has recently seen explosive growth thanks to advancements in computer hardware. A major milestone was the 2022 release of ChatGPT-3.5, a large language model (LLM) capable of generating human-like text. This powerful technology has found numerous applications in the medical field, from improving patient safety to aiding in diagnosis. Early studies indicated that ChatGPT performs remarkably well across the entire clinical workflow, including differential diagnosis, test recommendations, diagnosis, and treatment management, making it one of the most promising AI tools for doctors.
In the past year, the AI landscape has evolved rapidly. ChatGPT has been upgraded to version 4.0, and several powerful Chinese LLMs, such as Doubao and ERNIE Bot 3.5, have gained widespread use. However, the performance of these Chinese models in complex clinical scenarios had not been thoroughly evaluated. This study aimed to bridge that gap by comparing two leading Chinese LLMs with ChatGPT-4 and human doctors to assess their real-world application value in medicine.
Pitting AI Against AI A Comparative Study
To test the models' clinical acumen, researchers designed a comprehensive study using simulated patient cases. The AIs in the spotlight were Doubao, developed by ByteDance, and ERNIE Bot 3.5 from Baidu, alongside OpenAI's ChatGPT-4.
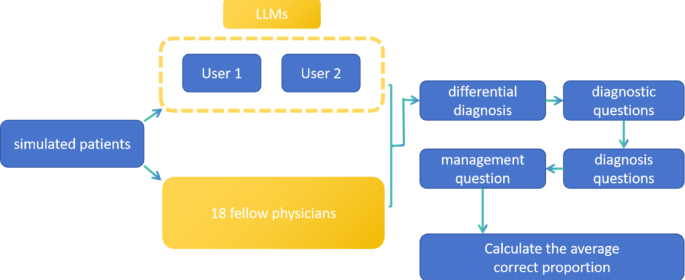
The study utilized 29 standard cases from the Merck Manual, which represent common clinical scenarios complete with patient history, physical exams, and lab results. These peer-reviewed cases were fed to each LLM, followed by a series of multiple-choice questions designed to mimic a doctor's thought process. The questions covered four key areas:
- Differential Diagnosis: Identifying possible conditions that could explain the symptoms.
- Diagnostic Questions: Determining the next appropriate diagnostic steps.
- Diagnosis: Providing a final, accurate diagnosis.
- Management: Recommending the best course of treatment.
The models' performance was scored based on the proportion of correct decisions made for each question. To add a human benchmark, the best-performing AI model was then compared against 18 emergency medicine fellows who underwent the same test.
Key Findings AI Performance Unpacked
The results revealed a fascinating picture of the current capabilities of medical AI.
Chinese LLMs vs. ChatGPT-4
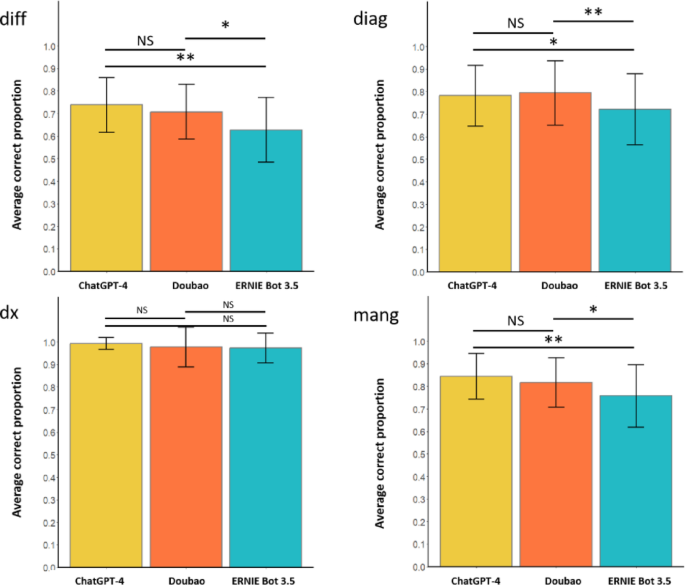
There was no significant performance difference between ChatGPT-4 and the Chinese model Doubao across all four clinical aspects. Both models showed strong capabilities. However, ERNIE Bot 3.5 generally performed at a lower level than ChatGPT-4 and Doubao in differential diagnosis, diagnostic questions, and management. Interestingly, when it came to making a final diagnosis, all three models performed exceptionally well, with accuracy rates above 97%, showing no significant statistical difference.
AI vs. Human Doctors
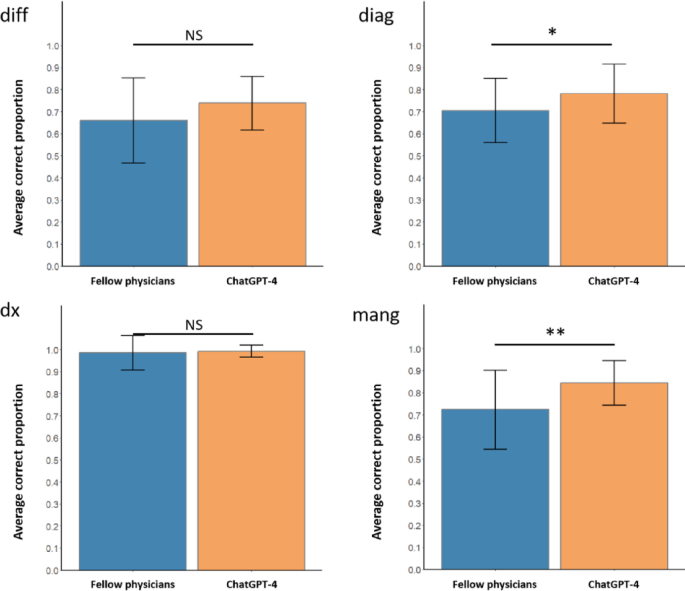
In the showdown between AI and human physicians, ChatGPT-4 (chosen as the best-performing model) was compared with 18 emergency medicine fellows. The results were striking. While there was no significant difference in their ability to make a final diagnosis or a differential diagnosis, the AI was superior to human doctors in recommending diagnostic tests and planning patient management.
The Rapid Evolution of AI
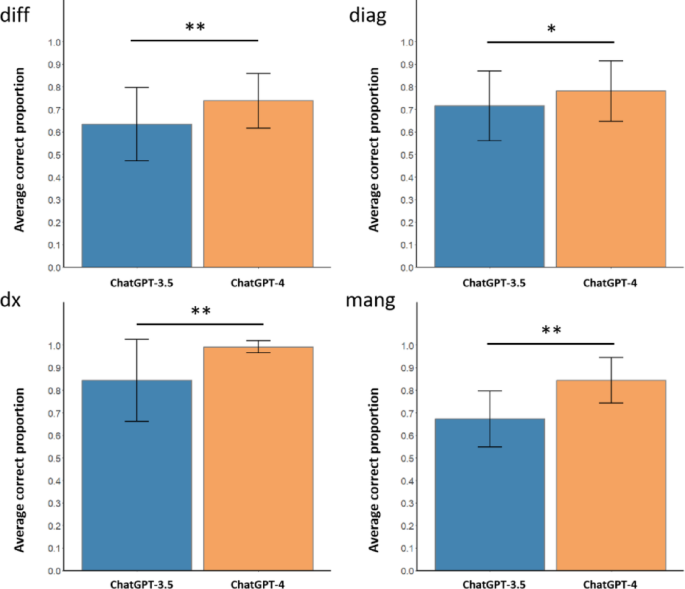
The study also highlighted the incredible pace of AI development. When comparing ChatGPT-4 to its predecessor, ChatGPT-3.5, the newer version showed superior performance in all four clinical areas. This rapid improvement in just a couple of years underscores the transformative potential of these models.
What Does This Mean for Healthcare
This study is the first to show that a leading Chinese LLM, Doubao, can perform on par with ChatGPT-4 in complex clinical workflows, suggesting that language and regional differences may not be significant barriers to performance. The models performed best when making a final diagnosis with sufficient information, achieving over 97% accuracy.
The finding that LLMs outperformed human emergency physicians in certain areas is promising, but it doesn't mean doctors are becoming obsolete. Human physicians work in collaborative, multidisciplinary teams, and AI currently lacks the ability to take a medical history or perform physical actions. Furthermore, LLMs can sometimes make critical errors with confident but incorrect reasoning—a phenomenon known as "hallucination." For example, one model incorrectly dismissed a serious heart condition based on flawed logic, an error that could be fatal in the real world.
Therefore, the most suitable role for LLMs today is as a clinical decision support tool, helping physicians fill knowledge gaps and consider a wider range of possibilities. The study did have limitations. The AIs may have been trained on the test cases, giving them an "open book" advantage over the human doctors. The small sample size also means more research is needed to validate these findings across different specialties and patient cases.
The Future of AI in Medicine
This research demonstrates that the Chinese LLM Doubao is a strong competitor to ChatGPT in the medical field. The fact that LLMs are outperforming human specialists in some areas and developing at an astonishing rate highlights their immense potential to revolutionize healthcare. While challenges remain, AI is steadily moving from a theoretical concept to a practical tool with the power to support doctors and improve patient care.
Compare Plans & Pricing
Find the plan that matches your workload and unlock full access to ImaginePro.
| Plan | Price | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | $8 / month |
|
| Premium | $20 / month |
|
Need custom terms? Talk to us to tailor credits, rate limits, or deployment options.
View All Pricing Details